This graphic shows the planned quotas (in dark blue) of independent enrollment for various universities in 2019 and the drop (in yellow) from a year earlier. [Source/People's Daily] Many universities halved their quotas for independent enrollment of high school graduates this year, as 89 out of 90 universities have announced stricter plans. Wuhan University of Technology in Hubei province reduced its quota by 77.8 percent — from 450 last year to 100 in 2019 — and Central South University in Changsha, Hunan province reduced its quota from 420 in 2018 to 120 this year. A total of 90 universities have the right to enroll high school students through their own exams and sets of standards, with 77 enrolling these students from across the country and 13 enrolling students from within their provinces, regions or municipalities. This year, universities have stipulated students holding patents or papers in fields were not qualified for independent enrollment, but awards at the provincial level or above in subject-specific competitions would be recognized. Universities have paid attention to the physical conditions of students this year, as a physical examination is a must and the results are added to the total score. Jin Ge, an official from Suzhou University in Jiangsu province, said the physical examination results are being added to guide students to realize they have to study well but still stay healthy. The national college entrance exam, or gaokao, has been a highly competitive and stressful test deciding the fate of high school students for many a year. In 2003, some universities were allowed to enroll students in specialties independently. As universities enlarged their independent enrollment quotas in recent years, problems appeared, such as faking papers and other issues. Earlier this year, the Ministry of Education asked universities to adopt stricter rules for independent enrollment; to avoid overreliance on criteria such as research papers, patents and competition results; and to limit the number of disciplines open for independent students.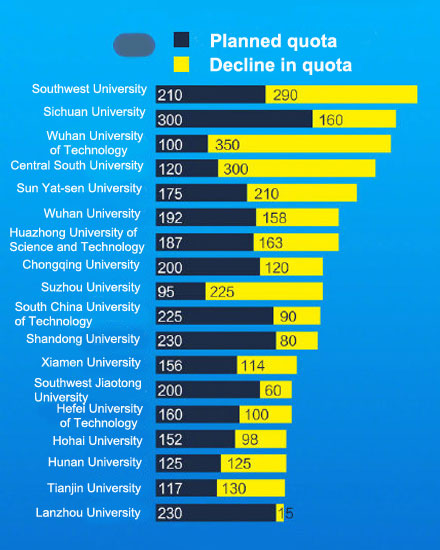
Universities tighten up rules for independent enrollment
Editor:李莎宁
Source:chinadaily.com.cn
Updated:2019-04-08 16:07:08
Source:chinadaily.com.cn
Updated:2019-04-08 16:07:08
Special
Contact
Welcome to English Channel! Any suggestion, welcome.Tel:0731-82965627
lisl@rednet.cn
zhouqian@rednet.cn











